
Welcome to SheddomeDB
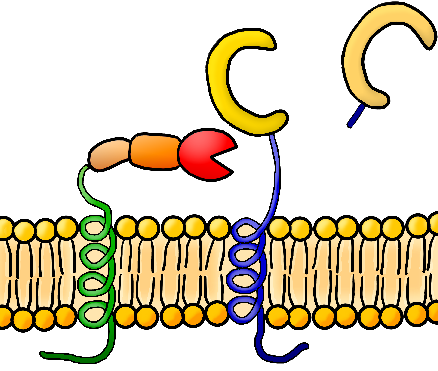
Ectodomain shedding is a cellular event involved in several biomedical aspects, such as immunology, development, diseases, and cancer. It is a proteolytic process in which the extracellular domain of membrane protein is cleaved by membrane proteinases, and the fragment is therefore released. Ectodomain shedding is considered one of the alternative secretory pathways for membrane proteins to be released into the extracellular environment or body fluid. Because ectodomain shedding sometimes accompanies diseases or cancers, the released fragments can be developed as biomarkers for preventive medicine.
Given the importance of ectodomain shedding in biology, our lab constructed SheddomeDB for ectodomain-shedding events in 2017. In order to construct this database, we manually surveyed the biomedical literature. Altogether, we summarized shedding events of 401 distinct proteins from 436 research papers, including substrates, responsible proteinases, released fragments and related diseases.